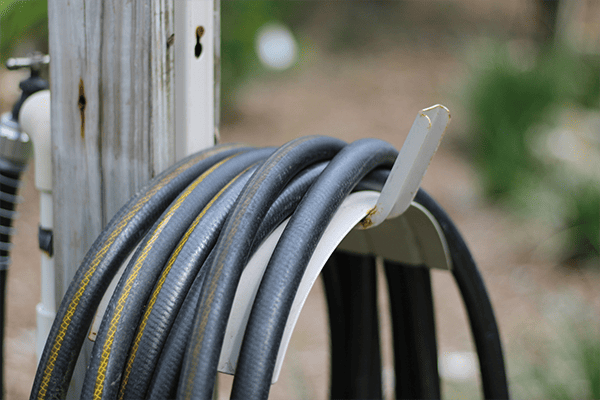
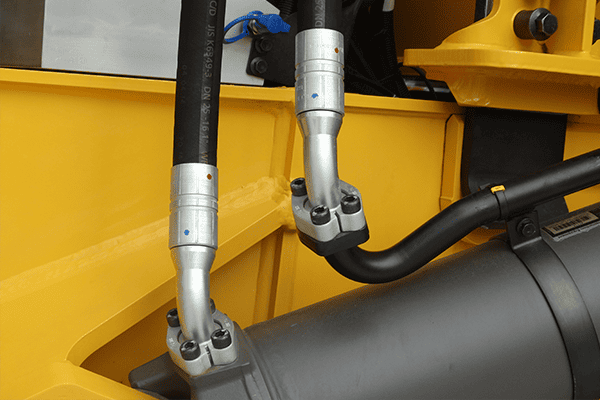
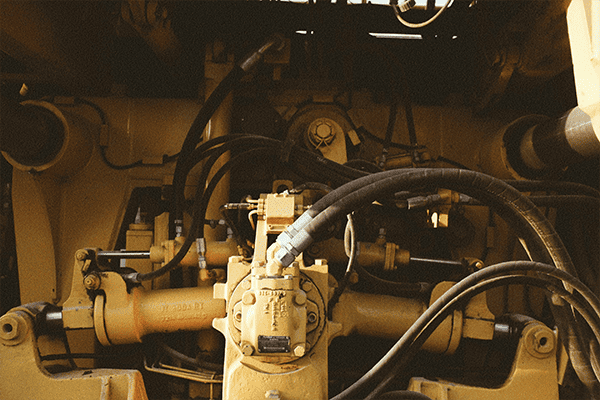
Hydraulic hoses must handle high pressures and harsh conditions. To perform reliably, they are built from three essential layers.
The three basic parts of a hydraulic hose are the inner tube1, reinforcement layer2, and outer cover3. Each layer serves a specific purpose.
Transition paragraph: Let’s break down each part and explore why they matter in the performance of hydraulic hoses.
What are the components of a hydraulic hose?
A hydraulic hose is made up of three primary components that work together to handle internal fluid pressure and external wear: the inner tube, reinforcement layer, and outer cover.
Each layer in a hydraulic hose is engineered to meet pressure, chemical, and environmental demands.
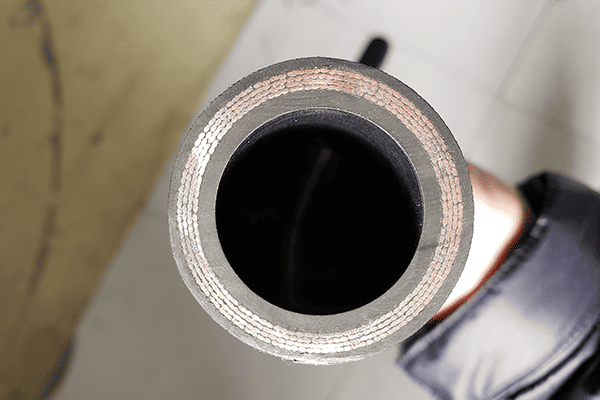
The inner tube carries the hydraulic fluid and must be compatible with oils and chemicals. It’s usually made from synthetic rubber or thermoplastic. The reinforcement layer provides the strength to resist high internal pressures. It can be made of braided or spiral steel wire or textile fibers, depending on the pressure rating required. The outer cover protects the hose from external damage like abrasion, UV exposure, and weather. It’s typically made from synthetic rubber that resists wear, oil, and ozone.
Components of a Hydraulic Hose
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Tube | Rubber or thermoplastic | Carries the hydraulic fluid, resists chemicals |
| Reinforcement Layer | Braided or spiral steel wire | Provides pressure resistance |
| Outer Cover | Synthetic rubber or thermoplastic | Shields from environmental damage |
Together, these layers ensure the hose is flexible, durable, and capable of operating under pressure.
What are the three layers of a hydraulic hose?
Hydraulic hoses are built in three distinct layers: inner tube, reinforcement, and outer cover. Each serves a specific and critical function.
The three layers work together to contain pressure, transmit fluid, and resist damage from external forces.

The inner tube is the core of the hose, and its job is to transport the hydraulic fluid without degradation. Materials used in the inner layer must resist oils, water, and chemicals depending on the system. The reinforcement layer is the backbone, built to handle the extreme pressure from within. For light-duty hoses, this may be a textile braid; for high-pressure systems, multiple steel wire braids or spirals are used. The outer cover acts as a protective skin. It shields the hose from cuts, heat, UV rays, chemicals, and other external threats.
Three Key Layers of Hydraulic Hose
| Layer | Role | Typical Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Tube | Fluid transfer | Nitrile rubber, synthetic rubber |
| Reinforcement | Pressure containment | Steel wire braid, spiral, textile |
| Outer Cover | Environmental protection | Neoprene, PVC, thermoplastic rubber |
These layers allow the hose to work safely and efficiently in tough industrial environments.
What is a hydraulic hose assembly?
A hydraulic hose assembly includes the hose and the end fittings permanently attached to both ends. It forms a complete unit ready to connect to hydraulic machinery.
A hydraulic hose assembly is a custom or standard combination of hose and fittings tailored for a specific hydraulic application.

While the hose alone handles fluid movement, it can't connect to a system without fittings. The assembly process includes selecting the correct hose size and type, then attaching crimped or reusable fittings using a hose crimping machine. The ends of the hose are cleaned and cut precisely before crimping. The fittings must match the application’s pressure and fluid requirements. Assemblies are tested for leaks and pressure ratings before use. Hose assemblies are commonly used in agriculture, construction, transportation, and manufacturing.
Components of a Hose Assembly
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Hose | Transfers fluid under pressure |
| Fittings | Metal connectors for attachment |
| Crimp/Seal | Ensures a leak-proof and secure connection |
Properly assembled hoses ensure efficiency, safety, and system reliability.
What are the basics of hydraulic hose?
The basics of a hydraulic hose include its construction, pressure rating, fluid compatibility, and application use. These aspects define the hose’s ability to perform in demanding environments.
Hydraulic hoses must handle specific pressures, resist chemicals, and operate under different environmental conditions.
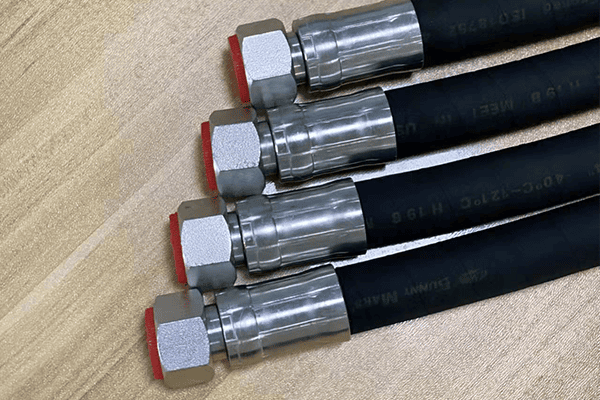
Hydraulic hoses are flexible tubes used to transmit fluid in pressurized systems. Their performance depends on correct construction and material selection. Each hose must be rated for the operating pressure and temperature of the system. Fluid compatibility is also essential—some hoses are rated for oil, while others are designed for water-based or synthetic fluids. The hose should also be flexible enough to route around machinery while withstanding vibration. Hose selection must match both technical requirements and working conditions.
Basic Considerations for Hydraulic Hose Selection
| Factor | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | Match to system max pressure + safety margin |
| Temperature Range | Operating and ambient temperature compatibility |
| Fluid Compatibility | Hose material must resist fluid degradation |
| Bend Radius | Must be flexible enough for the layout |
Knowing the basics ensures that you choose a hose that is both safe and suitable for your application.
What are the three basic types of hydraulic pumps?
Hydraulic systems use pumps to move fluid through hoses. The three basic types of hydraulic pumps are gear pumps, vane pumps, and piston pumps.
Each pump type delivers fluid at different pressure levels and flow rates to power hydraulic equipment.
- Gear pumps use interlocking gears to move fluid. They are simple, cost-effective, and reliable for low- to medium-pressure applications.
- Vane pumps use a rotor with sliding vanes that move fluid through the system. They offer smooth operation and are often quieter than gear pumps.
- Piston pumps are capable of very high pressures. They use a piston to move fluid and are used in high-performance systems like heavy construction and industrial machinery.
Types of Hydraulic Pumps
| Pump Type | How It Works | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Pump | Two gears rotate to move fluid | Low to medium pressure systems |
| Vane Pump | Rotating vanes create suction and pressure | Medium pressure, smooth, quiet operation |
| Piston Pump | Pistons move within cylinders to compress fluid | High-pressure systems, heavy-duty applications |
Selecting the right pump type is essential for efficient hydraulic system performance.
What are the common hydraulic hose fittings?
Hydraulic hose fittings come in various thread types and sealing methods. Common types include JIC, NPT, BSP, ORFS, and SAE fittings.
Common fittings vary by region and application, but they all ensure a secure, leak-free hydraulic connection.

Each fitting type is designed for different pressures, fluids, and system designs. JIC (Joint Industry Council) fittings feature a 37° flare and are widely used in North America. NPT (National Pipe Thread) fittings have a tapered design and are common in general applications. BSP (British Standard Pipe) fittings are more popular in Europe. ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) fittings offer excellent sealing in high-pressure systems. SAE fittings follow Society of Automotive Engineers standards and are common in vehicle and mobile hydraulic systems.
Common Hydraulic Fitting Types
| Fitting Type | Description | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| JIC | 37° flare, leak-resistant | Industrial and agricultural machinery |
| NPT | Tapered thread, basic sealing | General hydraulics, North America |
| BSP | British thread standard | European machinery |
| ORFS | Flat face with O-ring seal | High-pressure systems, leak prevention |
| SAE | Various automotive-based standards | Mobile and vehicle hydraulic systems |
Using the correct fitting type helps ensure compatibility, performance, and system longevity.
Conclusion
A hydraulic hose is built from three essential layers: the inner tube, reinforcement, and outer cover. Together, these components provide strength, flexibility, and protection to meet the demands of hydraulic systems.
-
Understanding the role of the inner tube is crucial for selecting the right hydraulic hose for your application. ↩
-
Explore the materials used in the reinforcement layer to ensure your hydraulic system can withstand high pressures effectively. ↩
-
Learn about the outer cover's protective role to enhance the durability and longevity of hydraulic hoses in harsh environments. ↩