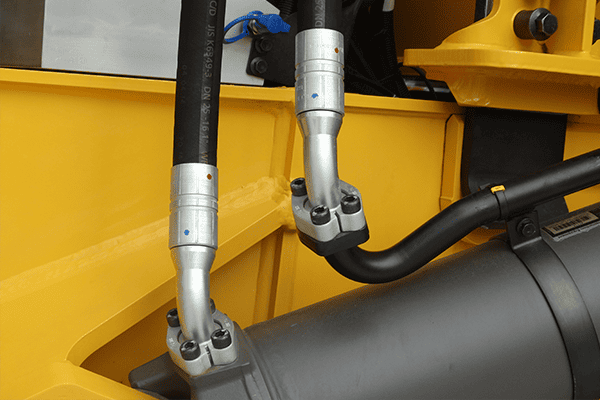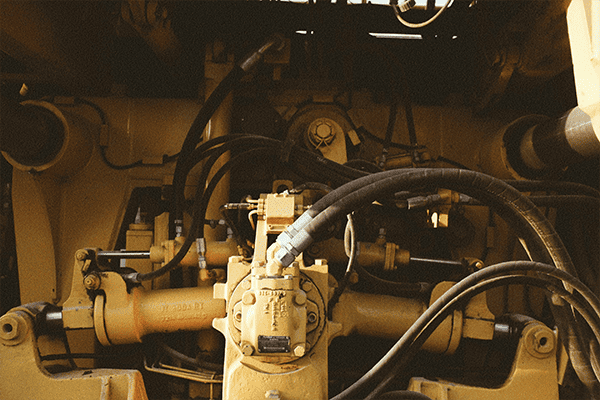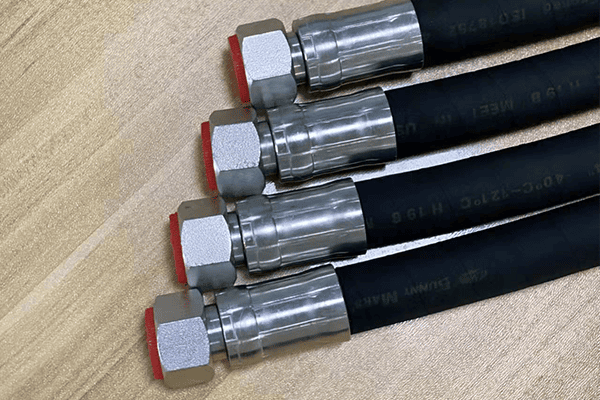
Straight hydraulic connections often cause system inefficiencies and failures. Learn why angled connections improve performance and protect components.
Straight hydraulic connections increase stress on hoses and fittings, leading to damage and inefficiency1. Angled connections enhance system reliability.
Straight configurations often cause leaks or stress. Let’s explore why angled connections are crucial for hydraulic systems.
What is the most common hydraulic problem?
Hydraulic leaks are the most frequent issue. Poor connections or wear lead to fluid loss2 and performance inefficiencies.
Leaks, pressure drops, and contamination are the most common hydraulic issues. Proper hose alignment minimizes these risks.
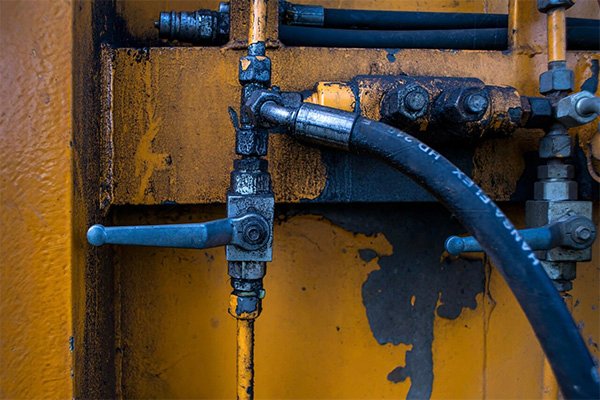

Why do leaks often occur in straight connections?
Straight connections often overstress hoses due to a lack of flexibility. This increases wear and leads to cracks or ruptures. Misaligned hoses amplify the strain on fittings, causing system damage. Properly angled connections reduce stress and extend system life.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid leakage | Overstressed connections | Use angled fittings |
| Wear and tear | Misalignment of components | Optimize hose routing |
| Pressure drop | Cracks in hoses | Maintain proper connections |
What is the angle of a hydraulic fitting?
Hydraulic fittings come in various angles to suit system designs and reduce stress3. Common options are 45°, 90°, and custom angles.
Choosing the right angle for hydraulic fittings ensures efficient fluid flow and prevents wear on hoses and components.

How do angled fittings optimize performance?
Angled fittings allow better routing and prevent unnecessary stress. Straight connections force hoses into awkward positions, reducing their lifespan. For example, a 90° fitting can simplify hose paths, avoid sharp bends, and improve fluid flow efficiency. This leads to better system performance and lower maintenance costs.
What is the correct way to install a hydraulic hose assembly?
Proper installation involves selecting the right angle fittings, avoiding tight bends, and securing hoses to prevent movement.
Install hoses with sufficient slack, avoid sharp bends, and use the correct fitting angles to ensure durability.
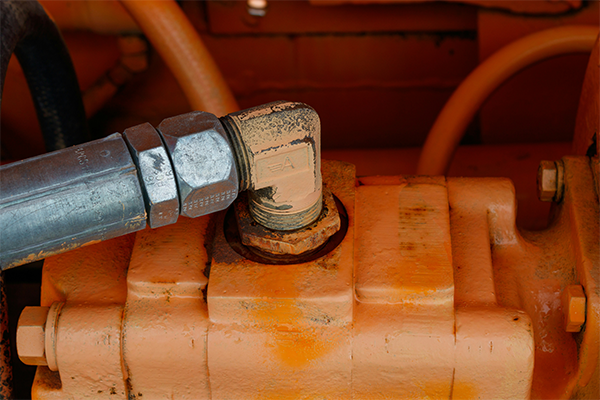

Steps for proper hydraulic hose assembly:
- Choose the right fittings: Select angled connectors that align with your system’s routing requirements.
- Avoid tight bends: Use a minimum bend radius to reduce stress.
- Secure hoses properly: Clamps prevent unnecessary movement.
- Test the system: Check for leaks and pressure stability.
Proper installation ensures that hoses last longer and the system operates efficiently. Misaligned hoses cause excessive wear, leading to frequent maintenance or system failures.
How does a hose bent at right angles cause hydraulic system noise?
Excessive noise results from turbulent fluid flow4, often caused by poorly designed bends or mismatched fittings.
Sharp hose bends create turbulence, increasing system noise and reducing efficiency. Angled fittings mitigate this issue.
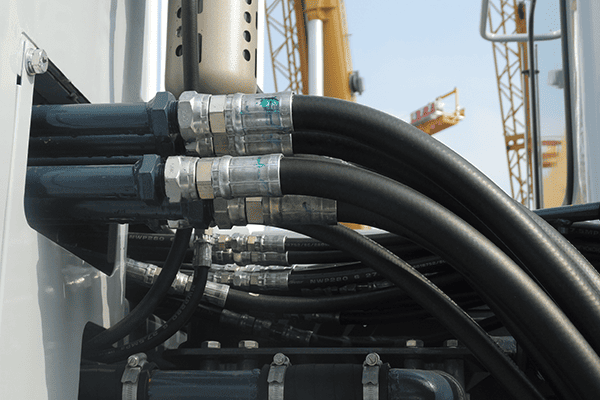
Why does turbulence increase system noise?
When fluid flow is forced into sharp angles, it disrupts smooth movement. This creates vibrations and noise. Over time, the turbulence can damage internal components, leading to expensive repairs. Angled fittings prevent turbulence, maintaining quieter and more efficient operations.
| Noise Source | Impact on System | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Sharp hose bends | Increased vibration | Use proper angled fittings |
| Turbulent fluid flow | Reduced efficiency | Ensure smooth hose routing |
Can you bend hydraulic hose?
Yes, but it must be within the manufacturer’s minimum bend radius to prevent damage and maintain efficiency.
Hydraulic hoses can be bent, but tight bends beyond the specified radius cause wear and reduce performance5.
Why is exceeding the bend radius harmful?
Hoses lose flexibility when bent too tightly, increasing stress on the reinforcement layers. Over time, this leads to leaks, pressure drops, and complete failure. Properly designed angled connections eliminate the need for extreme bends, ensuring the system’s longevity and efficiency.
What happens if you get air in hydraulic lines?
Air in hydraulic lines reduces performance, increases noise, and can cause erratic movements in machinery.
Trapped air in hydraulic systems leads to cavitation6, noise, and system inefficiencies. Bleeding the system resolves this issue.
Why is air in hydraulic systems a problem?
Air compresses under pressure, unlike hydraulic fluid. This creates inconsistent power delivery and can damage components. Properly sealed and aligned connections minimize the risk of air entering the system. Regular maintenance, including bleeding the lines, keeps the system running smoothly.
| Air-Related Problem | System Impact | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Cavitation | Reduced efficiency | Bleed the system |
| Increased noise | Vibrations in components | Check for leaks |
| Erratic movements | Inconsistent power output | Secure all connections |
Conclusion
Angled hydraulic connections ensure durability, reduce stress, and enhance efficiency. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for optimal system performance.
-
Learn why straight connections stress components and reduce hydraulic system efficiency. ↩
-
Discover how fluid loss impacts system efficiency and how to prevent leaks. ↩
-
Understand how angled fittings prevent damage caused by excessive stress. ↩
-
Learn how turbulent flow increases noise and reduces system efficiency. ↩
-
Find out why tight bends harm hoses and how to maintain optimal performance. ↩
-
Learn how cavitation reduces system efficiency and damages components. ↩